Sampling
Overview
Understanding the challenges and the nuances of selecting the right audience for your study.
Larry Vincent,
Professor of the Practice,
Marketing
MKT 512
February 10, 2026
Customer research process

Preparing for marketing research

Preparing for marketing research

Sampling
Case: Farapulse
Background:
New technology acquired by Boston Scientific (BSI) that improves the efficacy for patients who receive ablation for AFib. Ablation is an existing category of procedures that has been around for 30+ years. BSI wishes to gain share in category before competitors replicate their innovative technology that is in-market, and FDA approved.
Project:
Qualitative research requested on patients to understand perceptions of ablation, generally, and reaction to potential positioning concepts.
Question:
Who should participate in the research?

Two types of sampling
Probability
Probability sampling is a method where every member of the population has a known, non-zero chance of being selected for the sample. This method allows for statistical inferences to be made about the entire population based on the sample.
Non-Probability
Non-probability sampling is a method where the selection of participants is not determined by statistical chance. Some members of the population may have no chance of being selected, and the probability of selection for any individual is unknown.
Probability sampling
Characteristics
- Random selection
- Known probability of selection for each respondent
- Allows for calculation of sampling error and power
- Generally more representative of population
Common types
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified random sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Systematic sampling
Non-Probability sampling
Characteristics
- Selection based on subjective methods
- Unknown probability of selection
- Cannot calculate sampling error or power
- May not be representative of population
Common types
- Convenience sampling
- Purposive (Judgmental) sampling
- Quota sampling
- Snowball sampling
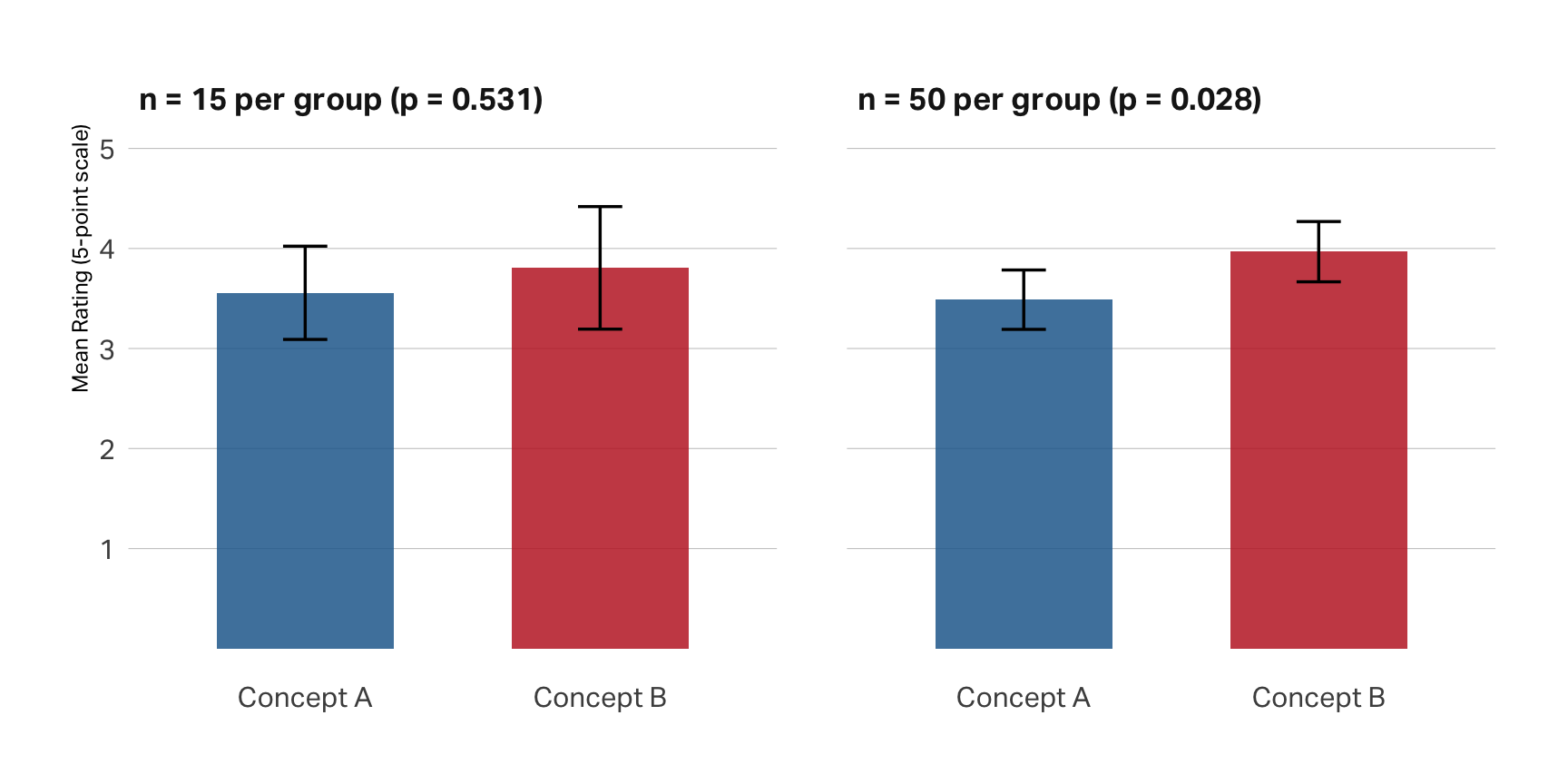
Why sample size matters
Scenario: You’re testing two positioning concepts for a brand. Concept B actually performs better than Concept A (true mean: 4.0 vs. 3.5). The difference is real. But can your study detect it?
General guidelines
- Clearly define target population before selecting sampling method
- Document your sampling process for transparency and replication
- Be aware of potential biases in your chosen method and address them in your limitations section
- For the qualitative project, focus on finding information-rich cases rather than aiming for strict representativeness
- For the survey, if using non-probability methods, try to diversify your sample as much as possible within your constraints
Airbnb
Background
In 2015-2016, Airbnb used post-stay surveys to measure guest satisfaction and improve service.
Research Method
Satisfaction surveys sent to guests after their stays. Survey asked guests to rate various aspects of experience. Ratings used to calculate satisfaction score.
Issue
Satisfaction scores showed over 90% positive ratings but qualitative feedback from customer service interactions and online reviews painted a different picture, suggesting many issues and complaints.
What Went Wrong?

Sampling for KCRW
Your challenge: zero budget, limited time, no access to KCRW’s internal databases.
- Define your target population first. Who does your research question require you to reach? Current members? Lapsed donors? Digital-only listeners? General market non-listeners? Each requires a different approach.
- Get creative with your frame. Social media communities, Reddit threads, campus intercepts, personal networks, snowball referrals from initial contacts. Every frame introduces coverage error — know what you’re missing.
- Screen ruthlessly. When you can’t control who enters your frame, screening questions are your quality control. Build a short screener that confirms participants match your target.
- Document your tradeoffs. You will not get a perfect sample. That’s fine. What matters is that you can articulate who you reached, who you missed, and why that matters for interpreting your findings.