Survey Research Fundamentals
Overview
Getting back to the basics of designing and fielding survey research.
Larry Vincent,
Professor of the Practice of Marketing
MKT 512
January 20, 2026
The Starting Point
Data = Truth + Mistakes
- Measurement Error
- Sampling Error
The information test
- What decision will this data inform?
- How specifically will I analyze this response?
- Can respondents answer this accurately?
- Will respondents answer this honestly?
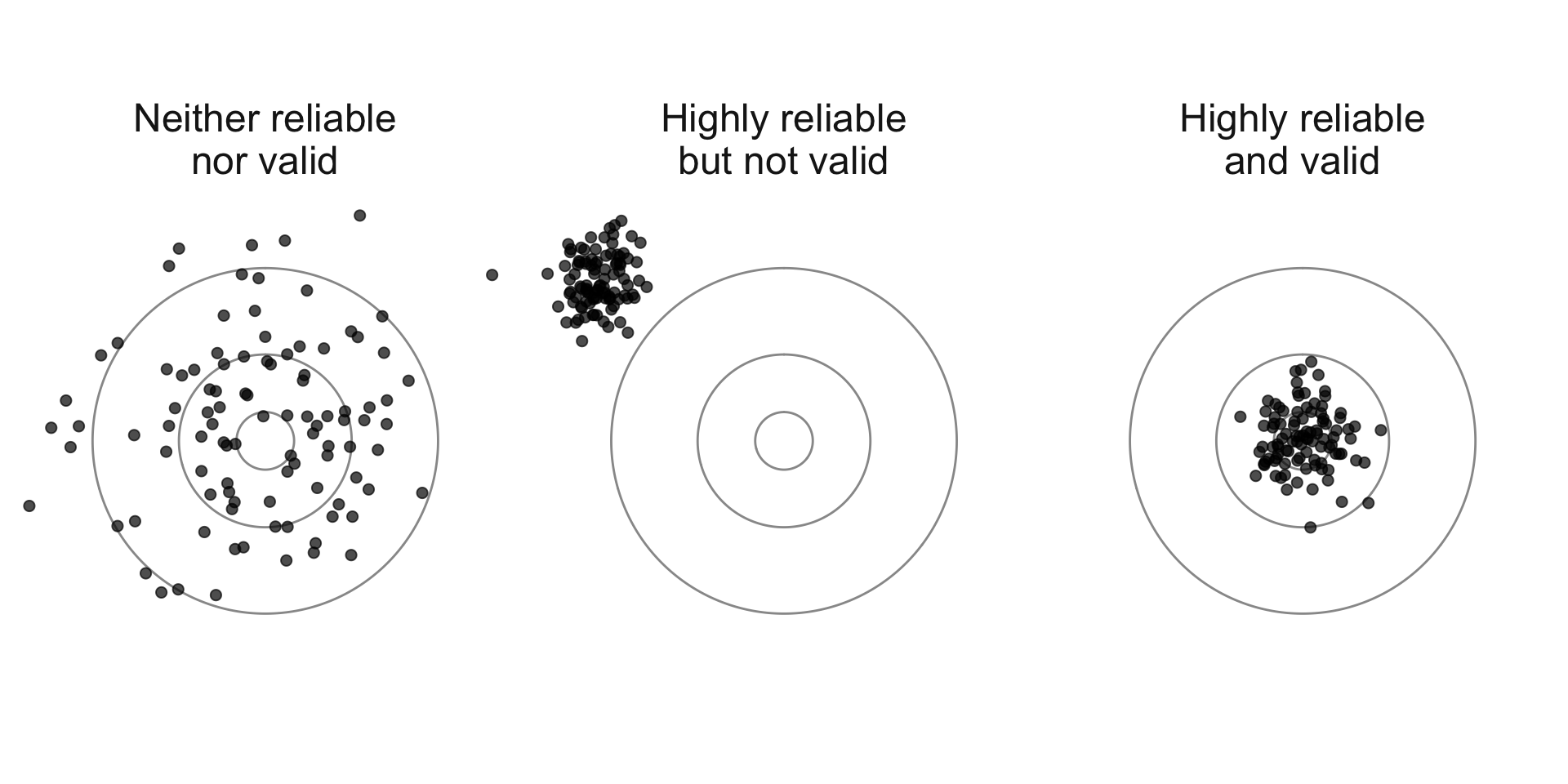
Validity
- Respondents must understand the question as intended
- Respondents must have the knowledge to answer
- Respondents must be able to recall the information
- Respondents must be willing to answer truthfully
- Response options must capture the true answer
Reliability
- Repeated measurements should yield consistent results
- Different respondents should interpret the question the same way
- The question should produce stable responses across similar contexts
- Measurement error should be random, not systematic
Validity vs Reliability
Question types
| Format | Use When | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Dichotomous | Binary situation, screening | “Have you purchased from Amazon in the past 30 days?” |
| Multiple Choice (single) | Discrete, mutually exclusive categories | “What is your employment status?” |
| Check All That Apply | Options not mutually exclusive | “Which devices do you use to stream video?” |
| Rating Scale | Attitudes, satisfaction, likelihood | “How likely are you to recommend?” |
| Ranking | Relative priority matters | “Rank these features in order of importance” |
| Open Text | Can’t anticipate responses; need depth | “What would make you more likely to renew?” |
Linking question types
to analyses
| Format | Data Type | Analytical Options |
|---|---|---|
| Dichotomous | Binary (0/1) | Frequencies, cross-tabs, chi-square, logistic regression (DV), any model (IV) |
| Multiple Choice | Categorical | Frequencies, cross-tabs, chi-square, dummy-code for regression |
| Check All | Multiple binary | Each option = separate dichotomous variable |
| Rating Scale | Interval | Means, t-tests, ANOVA, correlation, regression |
| Ranking | Ordinal | Specialized techniques, often converted to scores |
| Open Text | Qualitative | Coding, thematic analysis, NLP |
Best practices
1. Be clear and precise
Q. How many cups of coffee do you drink in a typical day?
Q. How frequently do you drink coffee?
- Extremely often
- Very often
- Not too often
- Never
2. Avoid overlaps
Q. Which of the following categories best describes your total household income before taxes for 2025?
- Less than $25,000
- $25,000 to $50,000
- $50,000 to $75,000
- $75,000 to $100,000
- $100,000 or more
Q. Which of the following categories best describes your total household income before taxes for 2025?
- Less than $25,000
- $25,000 to $49,999
- $50,000 to $74,999
- $75,000 to $99,999
- $100,000 or more
3. Use natural and familiar language
These can all mean “sandwich” in different regions and within different ethnic groups:
4. Avoid wording that shows bias
Q. What did you dislike about the product you just tried?
Q. Did you dislike any aspects of the product you just tried?
- Yes
- No
Do you think Boeing did everything possible to ensure passenger safety before the 737 MAX incidents?
5. Avoid double-barreled questions
Q. Do you believe that McDonald’s has fast and courteous service?
- Yes
- No
Q. Select the items below that describe your beliefs about McDonald’s service?
(Select all that apply)
- Fast
- Courteous
- …
6. State explicit alternatives
Q. Would you buy pasta-in-a-jar if it were available in a store where you normally shop?
- Yes
- No
Q. If pasta-in-a-jar and canned pasta product that you are currently using were both available in the store where you typically shop, would you…
- buy only the canned pasta product?
- buy only the pasta-in-a-jar product?
- buy both products?
Satisficing
Choosing the first acceptable answer(s) rather than evaluating all options to find the best or most complete answer.
Managing satisficing
Q. Which of the following words or phrases describe Apple as a company?
(Select all that apply)
- Innovative
- Overpriced
- Reliable
- Trendy
- User-friendly
- Elitist
- Secure
- Environmentally responsible
- Customer-focused
Q. Which of the following words or phrases describe Apple as a company?
(Select up to three)
- Innovative
- Overpriced
- Reliable
- Trendy
- User-friendly
- Elitist
- Secure
- Environmentally responsible
- Customer-focused
Vetting questions
- Is this a key question?
- Will knowing this help in making the business decision?
- Can we get this information elsewhere?
- Is this something we already know?
- Is this similar to another question?
- Is it needed in order to analyze key questions?
- Is it needed for routing survey flow?
Question ordering
Threatening questions
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Socially undesirable behavior | Illicit drug use, alcohol consumption, risky sexual behavior |
| Illegal activity | Tax evasion, shoplifting, speeding |
| Financial status | Income, debt, bankruptcy |
| Health conditions | Mental health, STIs, chronic illness |
| Personal failures | Job loss, academic performance, divorce |
| Socially desirable behavior (overreported) | Voting, charitable giving, exercise |
| Private beliefs | Political views, religious practices |
| Embarrassing habits | Hygiene, pornography consumption |
Source: Bradburn & Sudman (1979); Alreck & Settle (2004)
Planning the flow
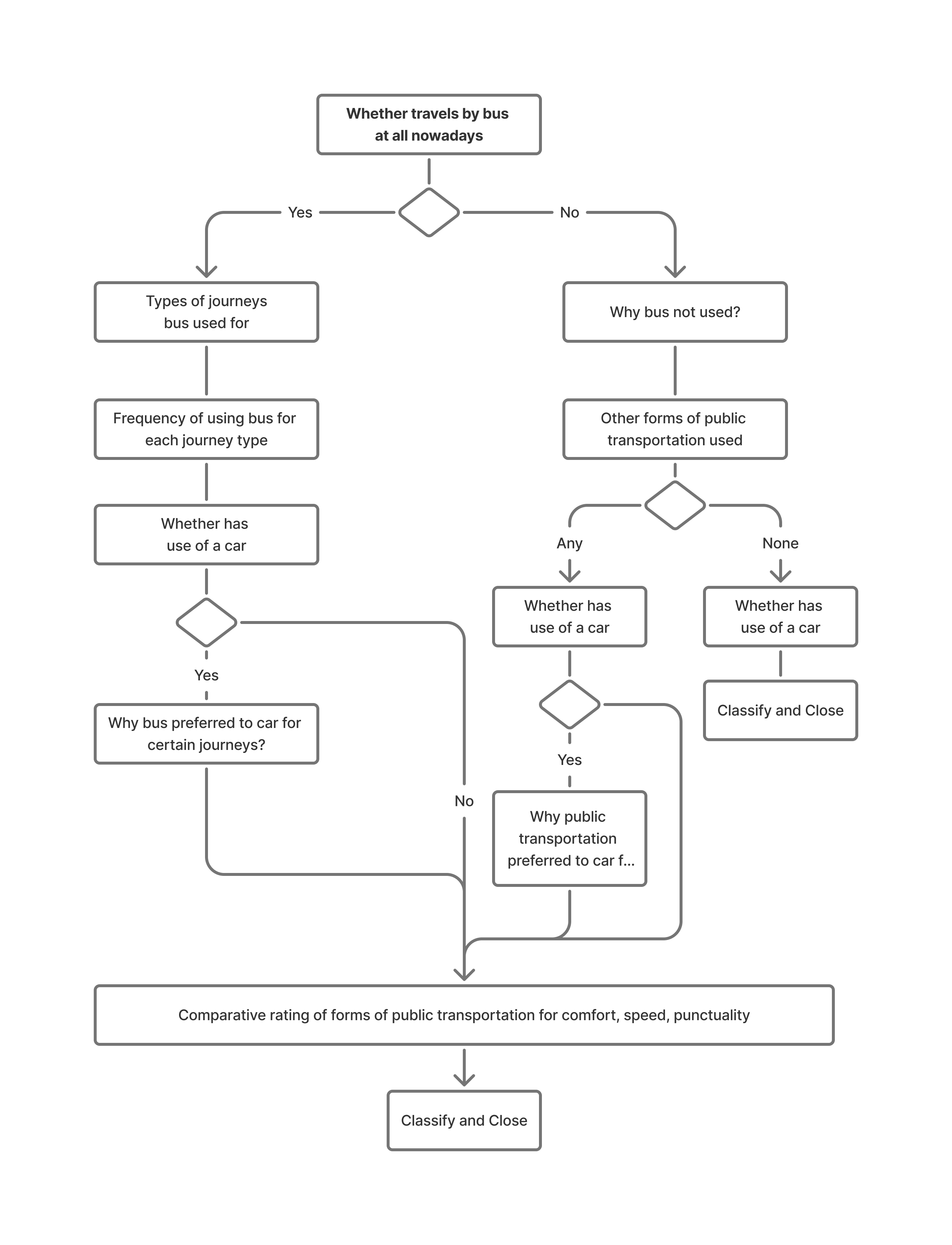 Source: Questionnaire Design, Ian Brace
Source: Questionnaire Design, Ian Brace
Typical survey flow

Within Screener:
- Terminate fast—don’t waste respondent time or your money on non-qualifiers
- Least sensitive qualifiers first (industry, role) before more sensitive ones (income, health status)
Within Main QRE:
- General category before branded content (avoid priming)
- Unaided before aided (awareness, associations)
- General before specific (funnel within topic areas)
- Sensitive questions later
Sampling Considerations
- Who is your target population?
Customers? Non-customers? Both? - What mix do you need? Balance by segment, demographics, region, or other characteristics
- How will you enforce that mix? Screening questions + quotas
- How will you reach them? Panel, customer list, social media, intercept
- What are the limitations? Convenience samples don’t generalize
Inspecting QREs
Qualtrics
Charrette I
